

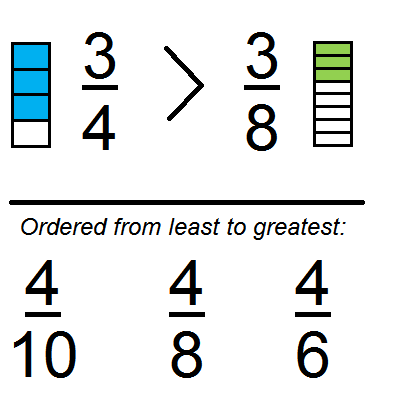
While the rules for fractional exponents with negative bases are the same, they involve the use of imaginary numbers since it is not possible to take any root of a negative number. If the exponent is an odd, positive integer, the result will again have the same magnitude, but will be negative. If the exponent is an even, positive integer, the values will be equal regardless of a positive or negative base. Exponents with negative bases raised to positive integers are equal to their positive counterparts in magnitude, but vary based on sign. They follow much the same rules as exponents with positive bases. It is also possible to compute exponents with negative bases. Grade 1 Multiplication and Division Exam Questions Multiplication and Division Time Exam Questions Time Writing, Simplifying and Ordering Fractions. Note that the calculator can calculate fractional exponents, but they must be entered into the calculator in decimal form. Input 5/7,2/1,17/159,3/5,45 set of fractions and order from least to greatest ie., 17/159 < 45 < 3/5 < 5/7 < 2/1 with the help of handy Ordering Fractions. It uses both the rule displayed, as well as the rule for multiplying exponents with like bases discussed above. Shown below is an example with a fractional exponent where the numerator is not 1. When an exponent is a fraction where the numerator is 1, the n th root of the base is taken. Thus, the only way for a n to remain unchanged by multiplication, and this exponent law to remain true, is for a 0 to be 1. Shown below is an example of an argument for a 0=1 using one of the previously mentioned exponent laws.
For many applications, defining 0 0 as 1 is convenient. When an exponent is 0, the result of the exponentiation of any base will always be 1, although someĭebate surrounds 0 0 being 1 or undefined. When an exponent is 1, the base remains the same. Similarly, when divided bases are raised to an exponent, the exponent is distributed to both bases. When multiplied bases are raised to an exponent, the exponent is distributed to both bases. When exponents are raised to another exponent, the exponents are multiplied. When exponents that share the same base are divided, the exponents are subtracted. When an exponent is negative, the negative sign is removed by reciprocating the base and raising it to the positive exponent. When exponents that share the same base are multiplied, the exponents are added. It also does not accept fractions, but can be used to compute fractional exponents, as long as the exponents are input in their decimal form. The calculator above accepts negative bases, but does not compute imaginary numbers. In the case where n is a positive integer, exponentiation corresponds to repeated multiplication of the base, n times. Both of them refer to the mnemonic for the logical order of operations for the mathematical expressions.Related Scientific Calculator | Log Calculator | Root CalculatorĮxponentiation is a mathematical operation, written as a n, involving the base a and an exponent n. The following examples illustrate how the PEMDAS convention addresses unclear mathematical problems.Įxample: 10 2 × ( 3 2 + 2 ) \frac\times\left(3^2+2\right) 2 1 0 × ( 3 2 + 2 ) = 35 35 3 5 Which is correct Pemdas or Bodmas? It is very critical to apply the correct order of operations in math to get the right answer when solving mathematical problems. The PEMDAS acronym convention implies grouping (parenthesis) first, then exponents, multiplication, division, and then addition and subtraction. This acronym is actually the PEMDAS rules which specify the exact order in which operations should be executed. PEMDAS is an acronym for an operating order convention to solve complex mathematical problems. The fraction calculator can add or subtract 2 fractions, 3 fractions and up to 9 fractions at a time, and shows the work to find common denominators, and simplify fractions to lowest terms or mixed number answers. Contribute to yuuurchyk/cppcalculator development by creating an account.
567 566 576 570 and verify it using the least to greatest calculator. PEMDAS calculator provides the solution with steps in a fraction of seconds. Calculator for adding and subtracting fractions with like or unlike denominators. For ascending or least to greatest order. Order of operations (PEMDAS) calculator is used to find the correct result of a math expression by following the accuarte sequence of operations.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
